What's inside
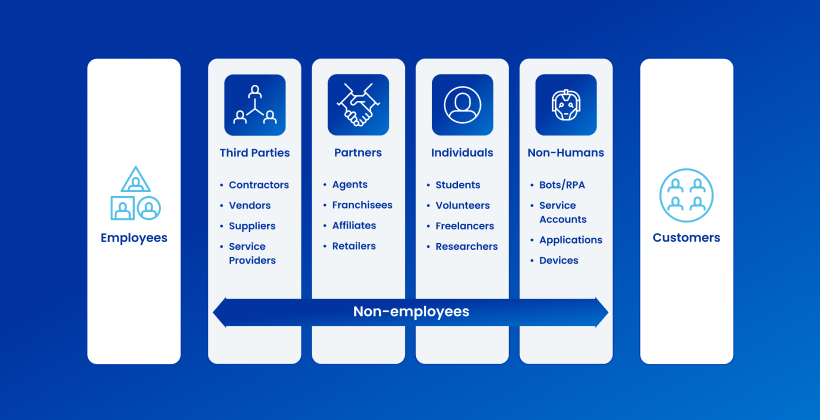
This paper reviews key findings from a global research survey to understand how companies manage non-employee and non-human identities and their respective access privileges. The research compared those approaches, processes, and corresponding workload efforts to that of managing employee identities. The survey then focused on the occurrence and ramifications of granting inappropriate access or failure to remove access when the work was completed.
Read this report to get detailed findings on non-employees and non-humans accessing applications, systems, and data, and what types of security issues arise from providing inappropriate access to third-party non-employees. You’ll also find additional insight on what type of processes companies rely on for non-employee identity and access processes (i.e., manual vs. automated), duplicate and orphan identity challenges, and more.
Key finding include:
- 54% of executives share that non-employees or non-humans with inappropriate access rights have resulted in a security issue
- 83% of organizations require a manual process to remove access from a non-employee when the working relationship ends
- Barely half (51%) of companies know at any point which non-human identities are accessing their systems